Wrist Fracture
(Fractura Radii Dist. Et Loco Typico)
What is a Wrist Fracture?
The wrist fracture is one of the most common fractures in the human body. Due to the constant further development and improvement of the available implants, the wrist-proximal radius fracture is increasingly becoming the domain of operative treatment.
Which fractures should be treated surgically?
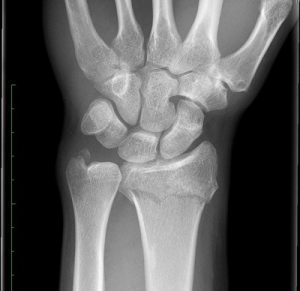
Wrist fracture
Surgery is recommended if the fracture has a displacement of the joint surface of more than 2mm and there is a significant axial deviation of the joint fragment. Often these symptoms are accompanied by a so-called “debris zone formation”. These criteria can be determined using X-ray and computed tomography images in order to make a clear indication for surgery.
Flexion fractures of the wrist (type “Smith”) always represent an indication for surgery in the event of fragment displacement.
Extension fractures (type Colles) can be treated with a splint or plaster cast if there is no or only slight displacement.
Which surgical method is used to operate on a broken wrist?
Plating is a suitable surgical procedure. An anatomically pre-formed titanium plate is used for this purpose, in which the screw heads provide maximum stability by tightening them in the plate. The procedure is performed under endoscopic control, i.e. under direct view into the joint with the rod lens.
When can I start physiotherapy?
The aftercare of the wrist fracture is functional, which means that you can move the joint immediately after the operation and start with physiotherapy.
Fracture of the scaphoid bone (Fractura os scaphoideum)
What is the scaphoid bone?
The scaphoid bone is a bone in the carpus. It lies directly on the radial joint surface, which means that it is often injured when falling on the wrist. If the scaphoid bone breaks, it leads to instability between the two carpal rows, which in turn can lead to severe arthrosis of the joint.
How is a scaphoid fracture treated?
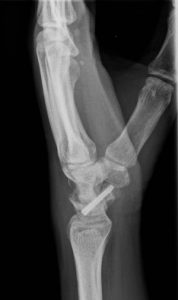
Scaphoid fracture OP screw
Non-displaced fractures of the scaphoid bone can be treated with immobilization. However, the scaphoid bone heals very slowly with immobilization alone. Plaster cast wearing times of 6-12 weeks are the rule.
Displaced fractures, as well as wrist-proximal scaphoid fractures (proximal pole fractures), are treated with a double-threaded screw (Herbert screw). With this special screw, the fracture can be placed under compression when screwed in to improve the chance of healing. Sometimes the introduction of autologous bone material is necessary.
